earth
12832 readers
42 users here now
The world’s #1 planet!
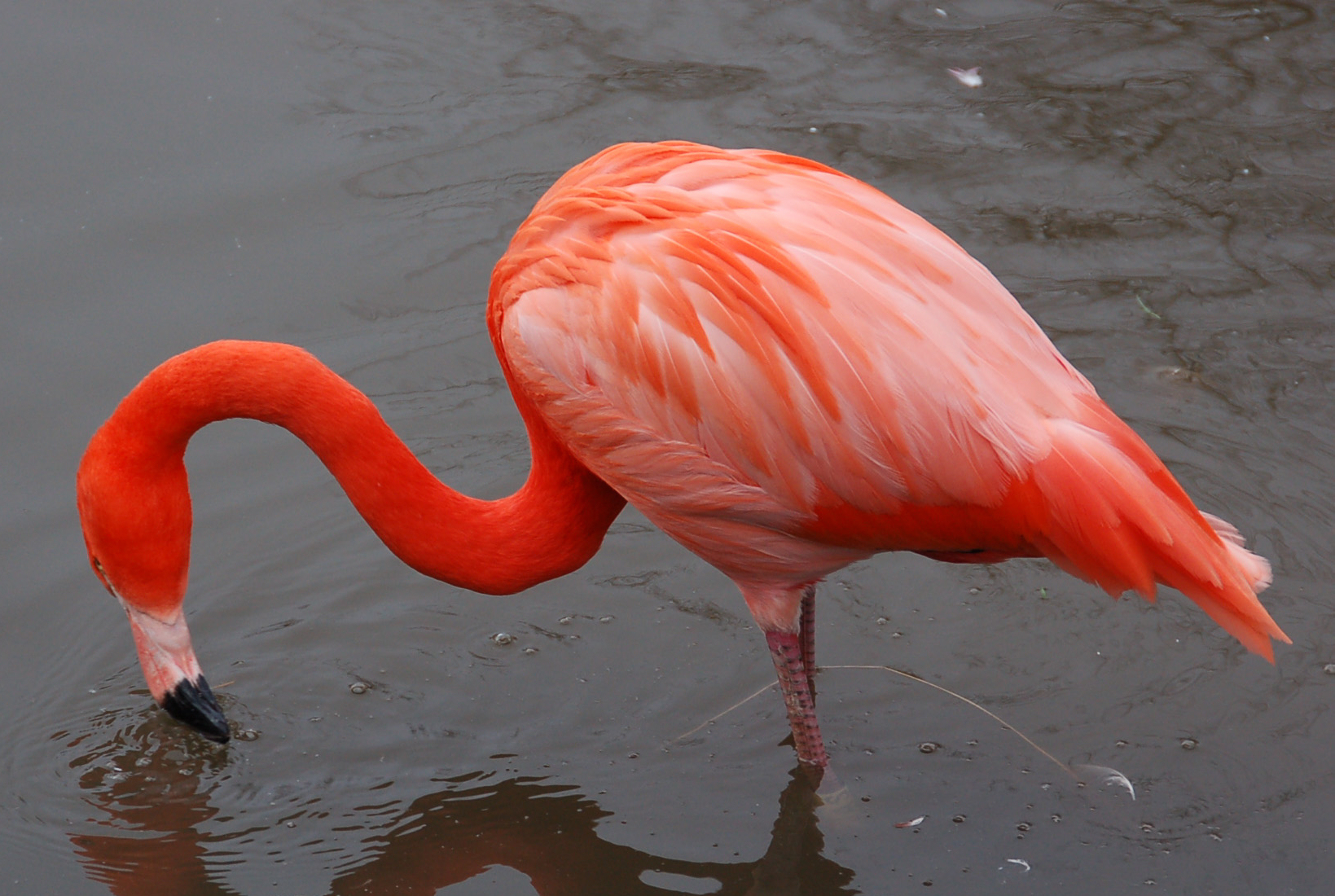
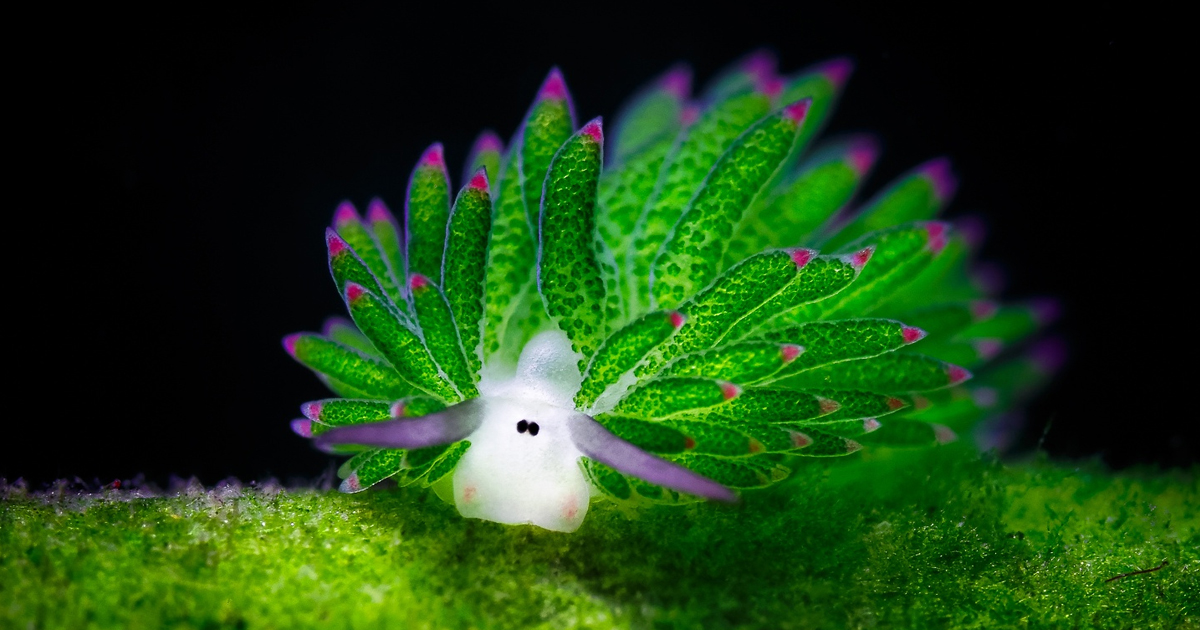
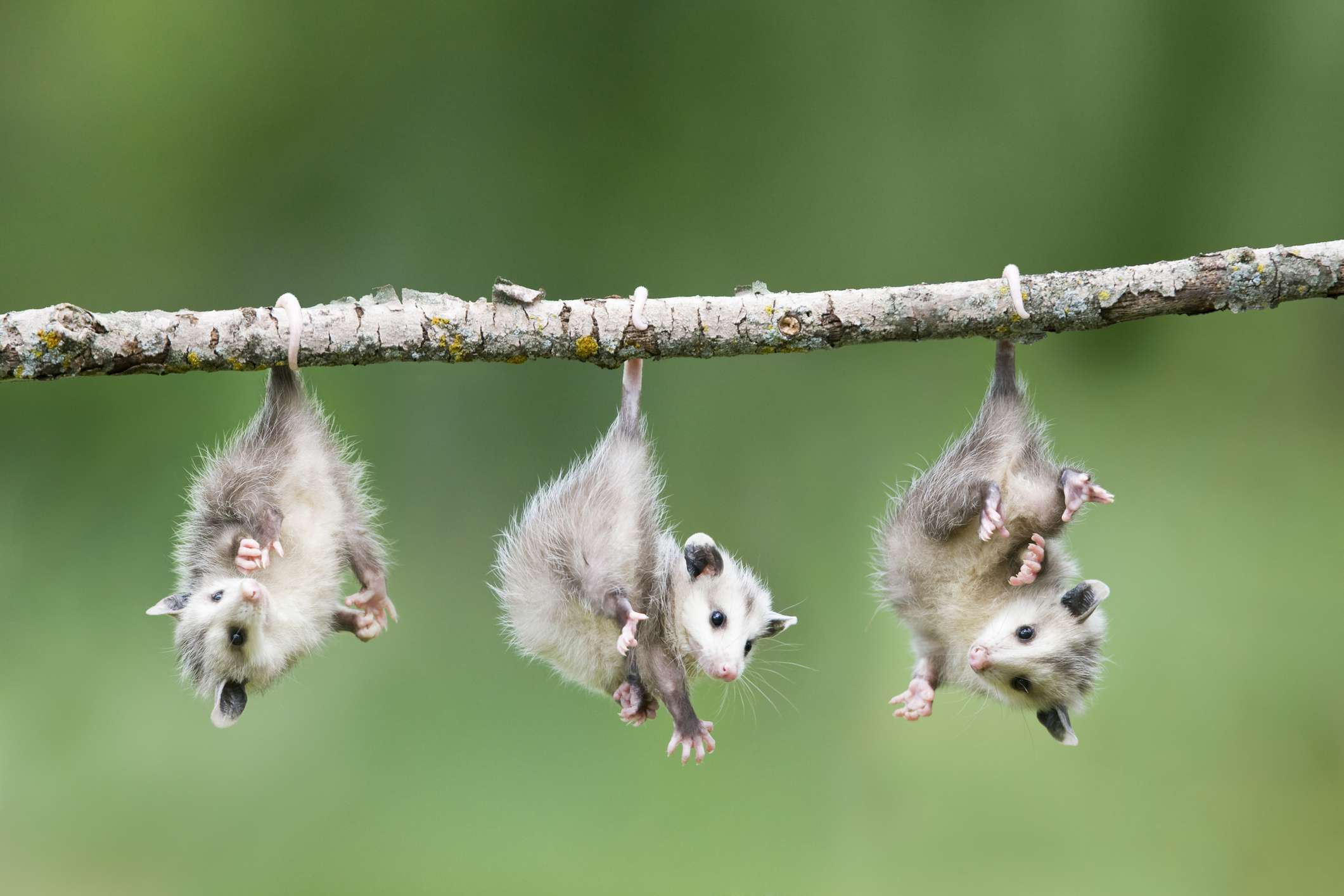
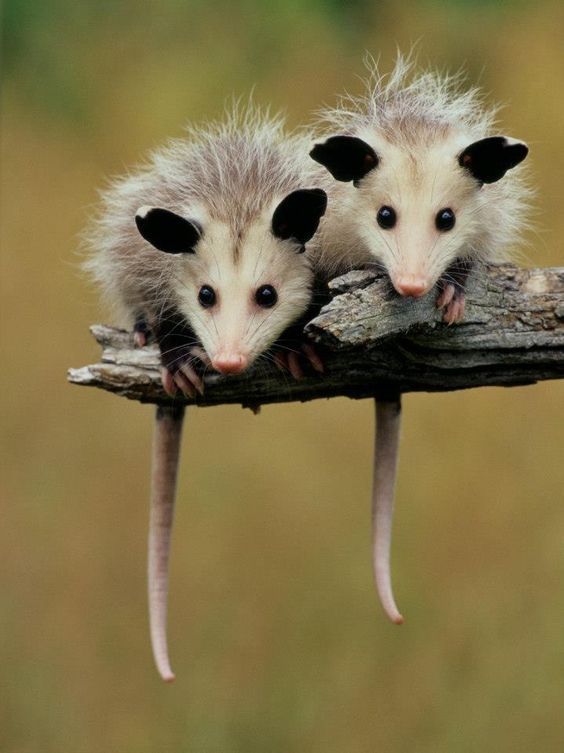
A community for the discussion of the environment, climate change, ecology, sustainability, nature, and pictures of cute wild animals.
Socialism is the only path out of the global ecological crisis.
founded 3 years ago
MODERATORS
1
26
How we got SLAPPed by Big Oil for over $300,000,000 - Greenpeace International
(www.greenpeace.org)
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
25
Whale sharks on collision course as warming seas may force them into shipping lanes – new study
(theconversation.com)
24
16
In Mexico, Totonac spiritual guides work with scientists to revive ecosystems
(news.mongabay.com)
25
view more: next ›