this post was submitted on 10 Apr 2024
437 points (100.0% liked)
Technology
38645 readers
540 users here now
A nice place to discuss rumors, happenings, innovations, and challenges in the technology sphere. We also welcome discussions on the intersections of technology and society. If it’s technological news or discussion of technology, it probably belongs here.
Remember the overriding ethos on Beehaw: Be(e) Nice. Each user you encounter here is a person, and should be treated with kindness (even if they’re wrong, or use a Linux distro you don’t like). Personal attacks will not be tolerated.
Subcommunities on Beehaw:
This community's icon was made by Aaron Schneider, under the CC-BY-NC-SA 4.0 license.
founded 3 years ago
MODERATORS
you are viewing a single comment's thread
view the rest of the comments
view the rest of the comments
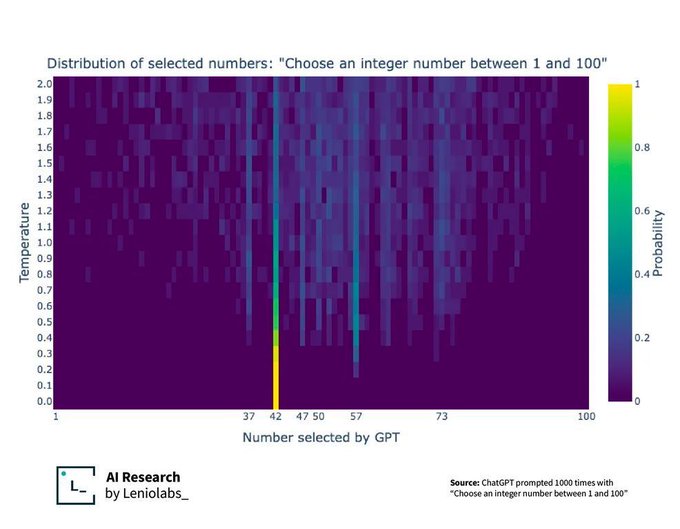
Probably just because it's prime. It's just that humans are terrible at understanding the concept of randomness. A study by Theodore P. Hill showed that when tasked to pick a random number between 1 and 10, almost a third of the subjects (n was over 8500) picked 7. 10 was the least picked number (if you ditch the few idiots that picked 0).
Maybe randomness is a label we slapped on shit we don't understand.
I remember watching a lecture about probability, and the professor said that only quantum processes are really random, the rest of things that we call random is just the human inability to measure the variables that affects the random outcome. I'm an actuarie, and it's made me change the perspective on how I see and study random processes and how it made think on ways to influence the outcome of random processes.
...which is kind of a hilarious tautology, because "quantum processes" are by definition "processes that we are unable to decompose into more basic parts".
The moment we learn about some more fundamental processes being the reason for a given process, it stops being "quantum" and the new ones become "it".
Even quantum just appears random I think. it's beyond our scope of perspective, it works in multiple dimensions. we only see part of the process. That's my guess though it could be totally wrong
it's a matter of interpretation, but generally the consensus is that quantum measurements are truly probabilistic (random), Bell proved that there can't be any hidden variables that influence the outcome
Didn't Bell just put that up as a theory and it got proven somewhat recently by other researchers? The 2022 physics Nobel Prize was about disproving hidden variables and they titled their finding with the catchy phrase "the universe is not locally real".
He proved it mathematically, but it was only recently confirmed experimentally
I see, thanks for the insight!
No problem! Interpretations of quantum mechanics are also still very much under discussion, and Bell's inequality only says that there are no local hidden variables. While QM very accurately describes observations so far, it's by no means solved, and there's a good chance that a new theory will upend much of it in the future
Interpretation for sure. Bells theory and then it being proven winning a Nobel prize to me only proves more we really don't understand the world around us and only perceive what we need to survive. And that maybe we should be less standoffish to ideas that change our current paradigm, because we obviously have a lot to learn.
Bells inequality is a statement about math, it gives an inequality that could only be violated if there were no local hidden variables (read: if measurements were truly random). That was a statement of math, which is rigorously provable. It took experimental confirmation, but we can now say with high confidence that there are no local hidden variables (i.e. there is no information hidden that we simply cannot measure, instead the outcome is only decided the moment you measure).
Global hidden variables are still an option, but they would require much of the rest of physics to be rewritten