Fedora is an almost bleeding-edge Linux distribution with an enthusiastic open source community behind it. While its association with Red Hat, and by extension, IBM, doesn't sit well with some, the distro has always been popular among desktop Linux users.
Almost six months after its earlier release, the Fedora developers have brought out the Fedora 42 release that's packed with many new upgrades.
Let's dive in without further ado. 😄
1. Anaconda is now Native Wayland

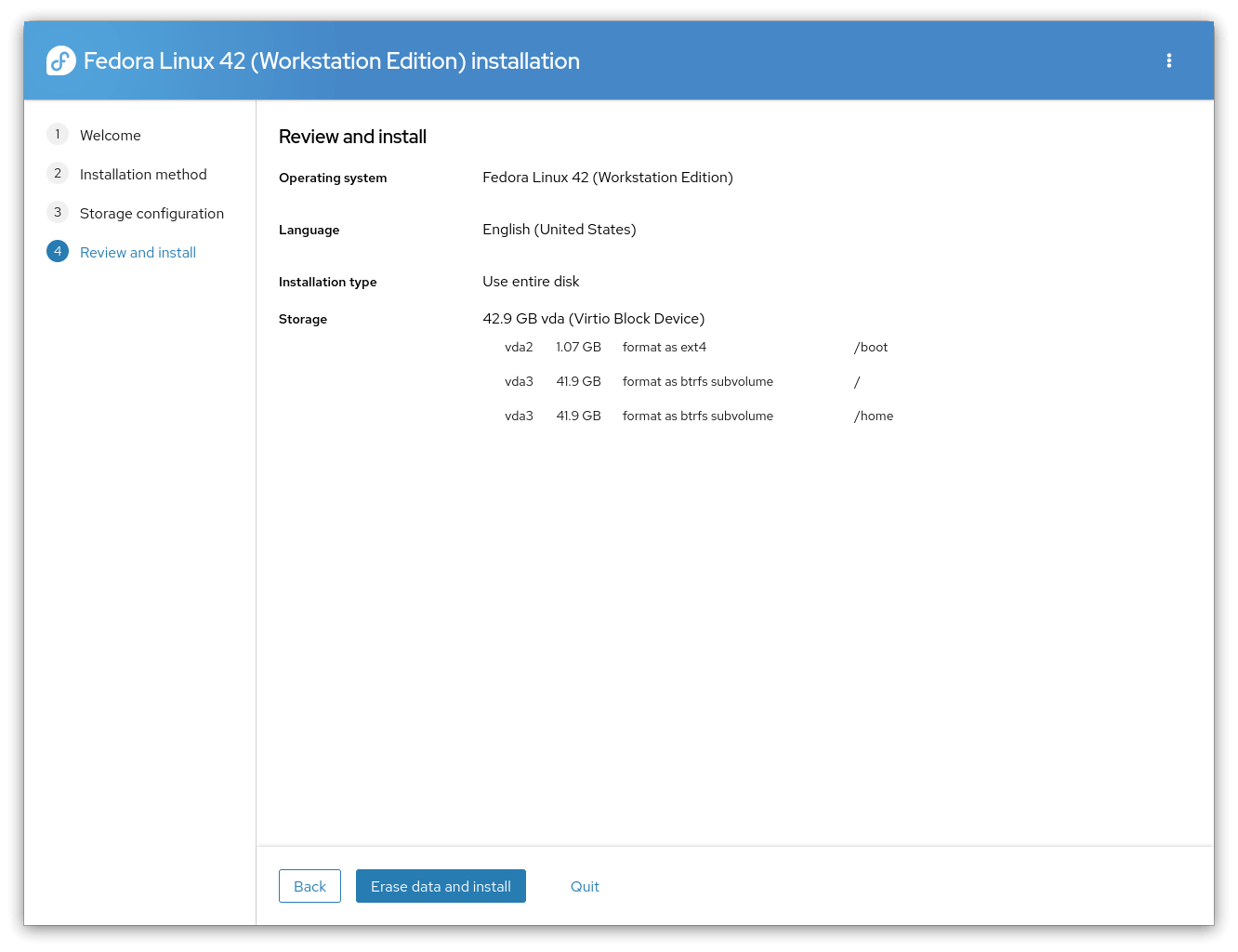
The Anaconda installer on Fedora 42 Workstation.
Starting Fedora 42, the default system installer, Anaconda, has gone Wayland-only, no longer supporting X11 sessions. It ships with improvements like better keyboard control, using GPT as the default partition table on all supported CPU architectures, and support for RDP, which replaces the earlier VNC implementation.
For disk partitioning, Anaconda now comes equipped with a new web user interface (Web UI) that simplifies the installation process with a guided partitioning feature, offering an automated experience where the user decides what kind of Fedora installation they want (e.g., single/dual-boot).
It is paired with a new "reinstall Fedora" option, which acts as a fallback if things go wrong during installation. This new installation experience has been made the default one for Fedora 42 and later.
2. KDE Plasma Edition
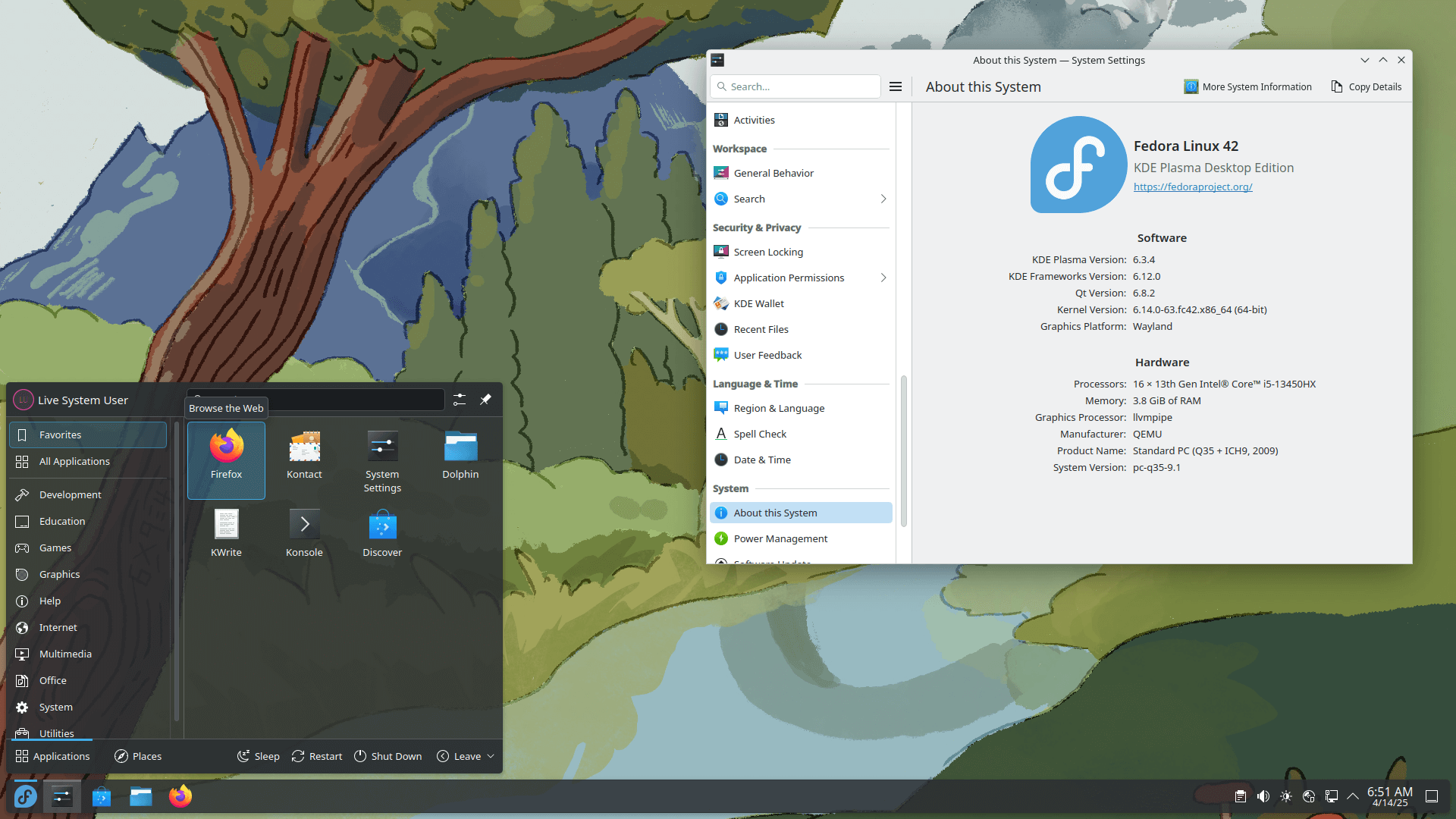
The KDE Plasma variant of Fedora is not a Spin anymore. Instead, it has been promoted to Edition, joining other flagship Fedora offerings like Workstation, CoreOS, IoT, and Server.
While this was confirmed as an alternative official edition for Workstation users, Fedora 42 is the first official release for it as an Edition. Currently, it comes packaged with KDE Plasma 6.3.4, KDE Frameworks 6.12.0, and a suite of KDE apps.
With this, Fedora now has the perfect alternative for Windows 10 users looking for a switch before the impending end of support arrives on October 14, 2025.
3. Fedora COSMIC Spin
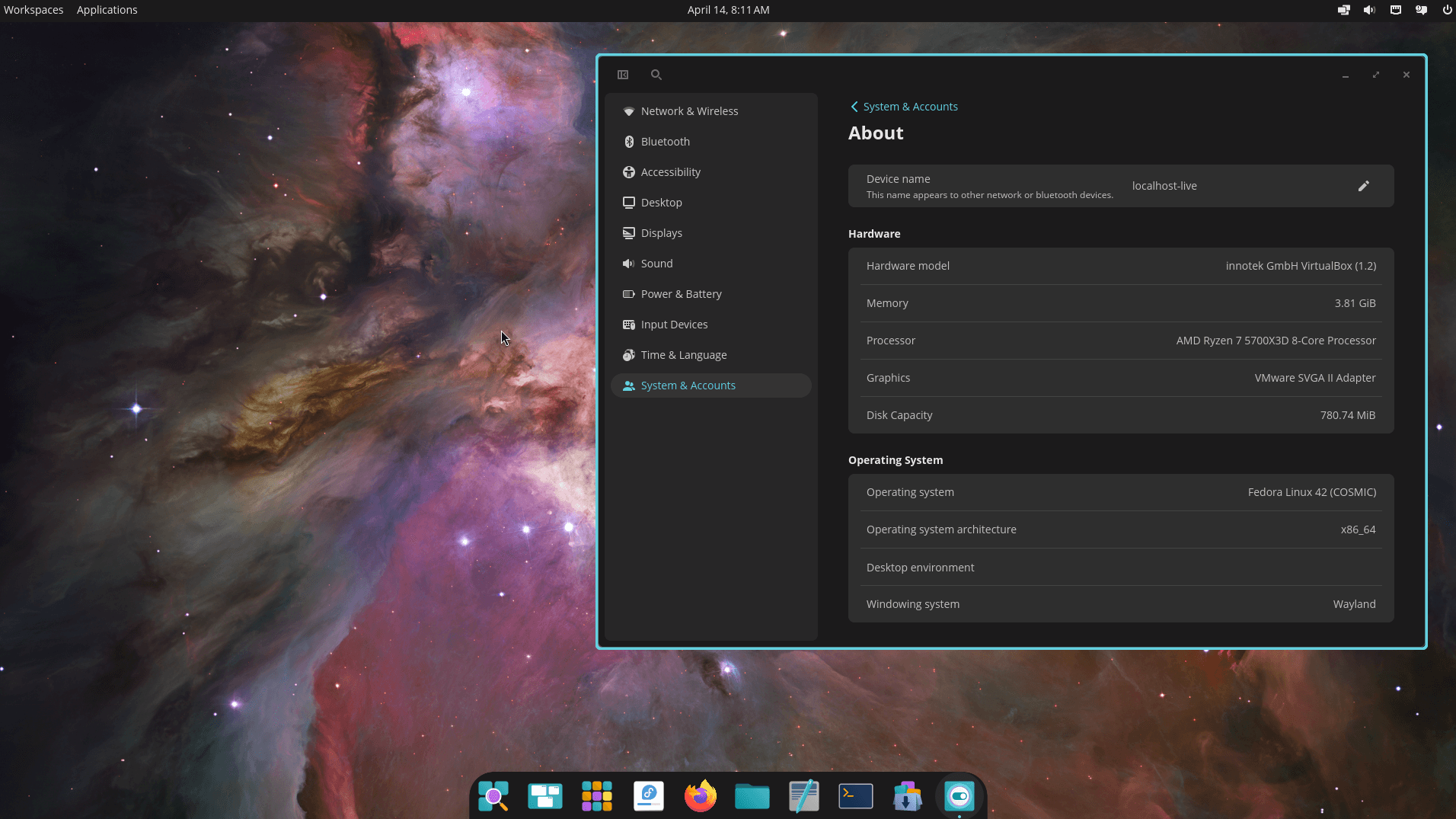
We knew this was coming, and it's finally here! Fedora COSMIC is a new Spin that provides a Rust-based desktop environment developed by System76, the makers of Pop!_OS.
Users who opt for this can expect the latest build of COSMIC, the COSMIC app suite, hybrid per-workspace window/tiling management, window stacking, and a wide range of customization options.
While this might not be as polished as the flagship Fedora offerings, it is still a good choice for those who like experimenting and trying new things.
4. Desktop Environment Upgrades
From left to right: Fedora 42 LXQt Spin, Workstation, and Xfce Spin.
The desktop environments also see some changes, with the Fedora LXQt Spin now coming equipped with LXQt 2.1.0 that introduces a new lxqt-wayland-session component, enabling support for seven Wayland sessions: Labwc, KWin, Wayfire, Hyprland, Sway, River and Niri.
For Workstation, there is now GNOME 48, which introduces new features like Wellbeing, Wayland Color Management, HDR support, Nautilus 48 as the file manager, better NVIDIA GPU support, and more.
Lastly, for the Fedora Xfce Spin, there is Xfce 4.20, which has brought about improvements like a better Xfce panel, refined power management, experimental Wayland support, and an upgraded Thunar file manager.
5. Core Tool Refinements
DNF5, the default package manager, now automatically removes any expired/obsolete keys during software installation or upgrades.
Similarly, Fedora 42 introduces RPM copy-on write, which leverages Btrfs' reflink capabilities to reduce I/O and CPU overhead during package decompression. Though, it is not enabled by default.
6. Linux Kernel 6.14
Powering all that is Linux kernel 6.14, acting as a powerful foundation with newly added support for AMD Ryzen AI NPU6, AMD RDNA 4 graphics, Ultra-High Bit Rate (UHBR) mode via DisplayPort for Intel Panther Lake (and later) CPUs, and loads of storage improvements.
You can check out our coverage to learn more.
Linux Kernel 6.14 Arrives With Performance Gains for AMD, Intel, and RISC-VThe second major Linux kernel release of 2025 has arrived! It's FOSS NewsSourav Rudra
It's FOSS NewsSourav Rudra
📥 Get Fedora 42
🚧You should back up any of your data and update your system's existing packages before flipping the switch to Fedora 42.SPONSORED
****Backup your PC in real time with pCloud.****pCloud will automatically save the folders you chose to the cloud. Any change you make will be applied to your pCloud account and your device.
Learn more about PC backup feature
Existing Fedora Workstation and KDE Plasma users can go into their respective software center apps Software/Discover and look for a banner or notification to get started with the upgrade process.
Users of other Fedora desktop builds will have to perform the upgrade using DNF. To get started, upgrade any existing packages on your system by running the following command and rebooting:
sudo dnf upgrade --refresh
Next, download the required packages for Fedora 42:
sudo dnf system-upgrade download --releasever=42
Then, use the following command to launch the upgrade process, which will immediately reboot your computer:
sudo dnf system-upgrade reboot
Given that everything goes well, then your computer will reboot once again, taking you into Fedora 42. If you have any doubts, then you can refer to the official upgrade guide.
We also have a tutorial that shows the steps for upgrading Fedora version. It remains the same for newer versions, too.
How to Upgrade From Fedora 39 to Fedora 40This tutorial shows you how to upgrade the Fedora version to a new major release. It's FOSSAbhishek Prakash
It's FOSSAbhishek Prakash
For fresh installations, you will find Fedora 42 ISOs for various CPU architectures on the official website. There are separate images for Workstation, KDE Plasma and the various Spins.
Fedora 42
You can refer to the official release notes and the changelog for learning more about this Fedora release.
💬 This release offers many nice things; I will be upgrading to it soon. What about you?
From It's FOSS News via this RSS feed
















 ParticleOS' GitHub repository.
ParticleOS' GitHub repository.